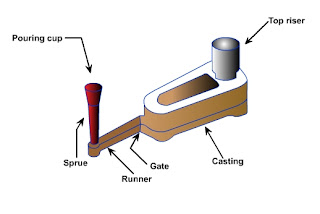
Pattern is an mirror image of the casting, when it is used with suitable moulding material it forms a cavity called as mould.
When this cavity is filled by molten metal and after solidification we get the desired casting.
Some allowance are provide in the pattern. They are as:
a. Allowance for shrinkage of metal.
b. Allowance for machining.
c. Draft allowance for easy removal of sand.
d. Core prints in the form of extra projections to produce seats for cores.
Tools used for making the pattern includes the tools already discussed in carpentry shop i.e. planes such as rib bet plane, block plane, router plane, plough plane, spoke shave, draw knife etc. the saw such as coping saw, bow saw, meter saw etc. the measuring and marking tools such as carpenter’s scale or folding rule, dividers, trammels, calipers and miscellaneous tools such as gauges, files etc.
Pattern material:
The most common material for making a pattern is wood due to some advantages:
• It is economical and easily available.
• Easy to convert in required shape and sizes.
• Light in weight and good finish is obtained only by planning.
• Can be preserved for a long time.
There are some short comings also in case of wood for example wear and tear for wooden item is more. It is effected by the atmospheric variations, due to this defect such as bending/warpage. Crooks etc. may develop in the patterns. Due to this life of wooden pattern is lesser than the other materials. Normally the wood used for pattern making are pine, deodar, teak, shisham etc.
Plaster:
Plaster of paris can be casted very easily to any shape. It has a very high compressive strength and can be used to make patterns of smaller sizes with close dimension control. It has the property that it expands on solidification. In case proper plaster is selected the effect of shrinkage is automatically neutralized.
Metals:
It is used when pattern are made in mass production with more accuracy. It overcomes almost all the shortcomings of wood. There are some limitations also in the use of metals.
They are as:
• In comparison to wood it is costlier.
• In this case machining is required which will increase the cost of pattern.
• It is heavier as compared to wooden pattern.
• It is affected by atmospheric corrosion due to which treatment is a must which increase the cost.
The metals used for making the patterns are:
a. CAST IRON:
It is economical. It can be casted to any shape having good machinability, resistance to abrasion, gives better surface finish, it is very heavy.b. BRASS:
Used for making patterns of smaller sizes. It has more strength, more resistance to corrosion, can be machined very easily, suitable for good surface finish, can be casted into any shape. It is heavier than cast iron.c. ALUMINIUM:
Pattern of bigger sizes are made by this metal. Since the weight is less and it is economical. It can be casted and machined easily for better finish. It is not as stronger as other metals.4. Plastics:
Plastic is used for making a pattern due to the properties lighter in weight, more strength with lesser wear, gives better finish and low shrinkage during melting also mot much costlier. Plastic that are used for pattern making are called thermosetting resins and phenolic resins. Initially the moulds are made from plaster of paris then the resin is poured in moulds at a particular temperature, the resin solidifies for getting plastic patterns.
5. Wax:
In this the mould is made into two halves and the wax is poured in this. The cooling of the die takes place by circulation of water. After setting, the die is separated and the pattern is taken out.
FACTORS AFFECTING THE SELECTION OF PATTERN MATERIAL
These are the points that must be considered while selecting materials for the pattern.a. Rate of production of casting.
b. Moulding is done manually or by machine.
c. What are the casting methods.
d. Accuracy and surface finish required in castings.
Master patterns:
It is used for making moulds for castings. It is a wooden pattern having both the shrinkage allowance and the machining allowance. Suppose aluminium is used to make moulds for brass castings. So aluminium pattern should have dimensions greater than brass casting equal to shrinkage that takes place while casting and machining allowance for processing the casting.PATTERN ALLOWANCE
Shrinkage allowance:
Most of the metal have a tendency to contract during solidification of the metal. The amount of shrinkage also differs from metal to metal, the factors that affect the shrinkage are temperature while pouring the metals, material of the mould specifications of the casting, method of moulding, casting material.
Machining allowance:
Machining may be required by the casting, may be partially or fully. In drawing the portion to be machined is identified and in those portions machining allowance is also provided, apart from shrinkage allowance. Machining allowance also depends upon casting metal, machining methods, specification of casting and the finish required.
Draft allowance:
Pattern are given slight taper on all vertical surfaces, this taper is draft allowance. This is either in degrees or linear measurements and it is provided in internal and external surfaces. It is provided for easy withdrawal of the pattern. Draft allowance depends upon its vertical height and moulding method.
Shake allowance:
Before withdrawal of the pattern first of all it is shaken so that it is free from adjoining walls, due to this size of mould cavity increases so a negative allowance is given to pattern.
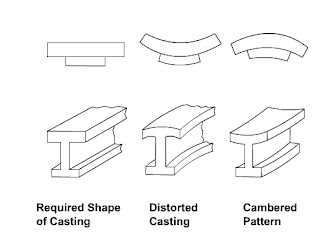
Distortion allowance:
There are certain casting in which the cooling of the metal is not uniform throughout the casting due to very complicated shape. Due to this there is distortion in the castings. To minimize its effect distortion in opposite direction is given in the pattern.
Movement of mould wall:
Due to excessive heat the walls of the mould have a tendency to move, this movement of the wall affects the final size of the castings. In order to minimize the effect, allowance is added in the pattern and it is also controlled by controlling three parameters moulding sand composition, density and temperature of molten metal.
USE OF A PATTERN
a. To form a cavity of proper shape and size in the moulding material so that required casting is obtained by molten metal.
b. Providing seating surface for the cores that are used for making the cavity. This resting surfaces are called core prints.
c. To form several locating points that are used as reference points for checking dimensions of the casting and the measurement during machining.
d. It reduces casting defects.
e. It minimizes the cost of casting.










Auto Die Cast (India) makes strong and quality Aluminium Die Casting products at fair prices. Trusted by many industries for reliable service. Contact us today for the best casting solutions.
ReplyDelete