Array is an arrangement of same type of data at adjacent memory locations. Array is useful whenever large volume of data is to be processed and stored in the memory.
Suppose an average marks are to be calculated from all the students in the school. This is difficult to find the sum of marks of all students. In this situation an array is the best alternative. Its divided in two categories:
1. Single / 1-D Array
2. Multi-dimension Array
Single / 1-D Array
In this array data / values is stored under one name at adjacent memory location but with the array name position of element or number is attached in square brackets [], the variable which is attached to the array name is [] is called Subscript or an index 1-D array. It stores numbers in a single row or column.It means to represent an array having 10 elements the dimension will be ar[10] and to declare the array format is:
Data type array name [dimension]
int ar[100];
float ar[100];
double ar[100];
char ar[100];
One for loop is required to store number in the array and to name them.
Second for loop is required to print or process the numbers.
If an array has already initialised the only one for loop is required to print the series.
int ar[5]= {2,4,6,8,10}
float ar[5]= {1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4,5.5}
char ar[10]= Aman
/*Program to enter roll number of 5 good students with their marks and print in sequence*/
#include<stdio.h>#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int roll[5],marks[5],i;
printf("\n enter 5 roll numbers of 5 good students");
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&roll[i]);
}
printf("\n enter marks of 5 students");
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&marks[i]);
}
printf("\n rno. \tmarks:");
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
printf("\n %d \t%d",roll[i],marks[i]);
}
getch();
}
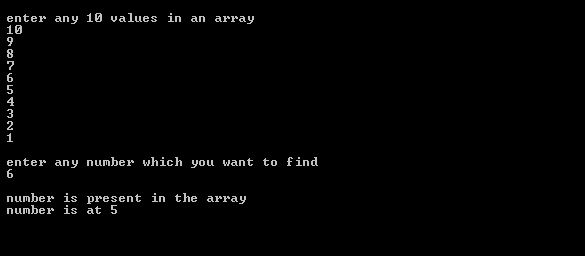
/*Program to enter any 10 number of his choice and find any number in the series with its position if present in it*/
#include<stdio.h>#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int ar[10],n,position=0,i;
printf("\n enter any 10 values in an array");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&ar[i]);
}
printf("\n enter any number which you want to find");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
if(ar[i]==n)
{
printf("\n number is present in the array");
position=i+1;
printf("\n number is at %d",position);
}
if(i==11)
printf("\n number is not present in the array");
getch();
}
/*Program to enter 10 number by the user and find the biggest value among that series with its position*/
#include<stdio.h>#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int i,big,position;
int a[10];
printf("\n enter any 10 int values");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
big=a[0];
for(i=1;i<10;i++)
{
if(big<a[i])
{
big=a[i];
position=i;
}
}
printf("\n biggest no is %d",big);
printf("\n position of largest no is %d",position);
getch();
}
Multi-Dimension Array
In this array numbers are arranged in rows and columns. It means in multi-dimension array row and column dimension should be specified with the array name while declaring in the array.int ar[row dimension][column dimension];
int ar[30][30];
It means while storing an array every element in the array has its name based on its row position and column position in the array.
It means two subscripts are required with array name and here 1st subscript stand for row and 2nd subscript for column. While storing array of order 2*2
Row subscript varies from 0 to 1
Column subscript varies from 0 to 1.
Such an array can be defined as:
One set of nested for loop is required to store numbers in the array and another set of nested for loop is required to print numbers in the array.
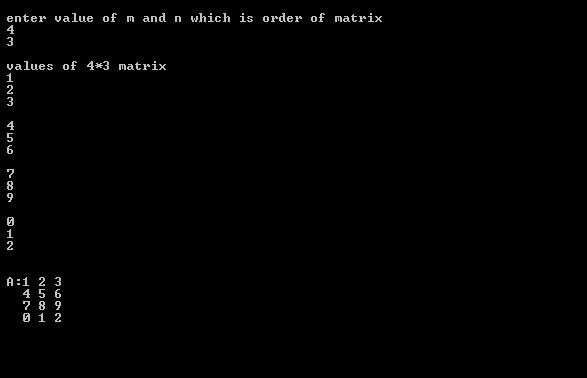
/* Program to print matrix of any order of your choice*/
#include<stdio.h>#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a[20][20],i,m,n,j;
printf("\n enter value of m and n which is order of matrix");
scanf("%d%d",&m,&n);
printf("\n values of %d*%d matrix",m,n);
for(i=0;i<m;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n A:");
for(i=0;i<m;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
printf("%d ",a[i][j]);
}
printf("\n ");
}
getch();
}
/*Program to enter two matrix of order 2*2 and find sum of matrix */
#include<stdio.h>#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a[2][2],i,j,b[2][2],c[2][2];
printf("\n enter 4 values of A");
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n A:");
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
{
printf("%d ",a[i][j]);
}
printf("\n ");
}
printf("\n");
printf("\n enter 4 values of B");
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&b[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n B:");
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
{
printf("%d ",b[i][j]);
}
printf("\n ");
}
printf("\n");
printf("\n C:");
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
{
c[i][j]=a[i][j]+b[i][j];
printf("%d ",c[i][j]);
}
printf("\n ");
}
getch();
}
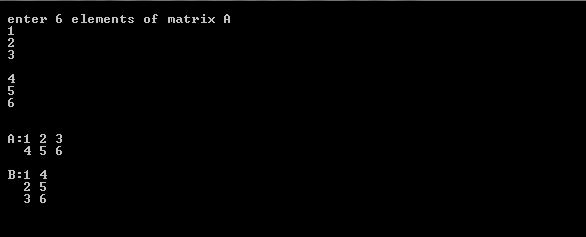
/*Program to enter elements of 2*3 matrix and find the transpose of that matrix */
#include<stdio.h>#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a[2][3],b[3][2],i,j;
printf("\n enter 6 elements of matrix A");
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n A:");
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
printf("%d ",a[i][j]);
}
printf("\n ");
}
printf("\nB:");
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
b[j][i]=a[i][j];
printf("%d ",b[j][i]);
}
printf("\n ");
}
getch();
}
/*Program to show matrix multiplication of particular order */
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a[2][2],i,j,k,b[2][2],c[2][2];
printf("\n enter 4 values of A");
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n A:");
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
{
printf("%d ",a[i][j]);
}
printf("\n ");
}
printf("\n");
printf("\n enter 4 values of B");
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&b[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n B:");
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
{
printf("%d ",b[i][j]);
}
printf("\n ");
}
printf("\n");
printf("\n C:");
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
{
c[i][j]=0;
for(k=0;k<2;k++)
{
c[i][j]=c[i][j]+a[i][k]*b[k][j];
}
printf("%d ",c[i][j]);
}
printf("\n ");
}
getch();
}







No comments:
Post a Comment