Showing posts with label call. Show all posts
Showing posts with label call. Show all posts
January 30, 2013
Friend Function in C++ (OOPs)
A Friend Function is a non-member function that can access private data’s. A friend CLASS is a class whose member functions can access another class i.e. private and protected classes.
Structures in C++ (OOPs)
Structure is the user defined data type which can store heterogeneous data i.e. data of different types. It means in structure member with all possible data type can be used and there is no restriction that elements of the structure are stored at adjacent memory locations. Structure is declared with key word struct followed by its name and then by block.
Pointers in C++ (OOPs)
Pointer is that variable which stores the memory address of another variable. It means pointer is itself a variable which stores hex-decimal address of the location.
January 23, 2013
Files Input/Output in C-language
A file is a place on the disk where the group of related data are stored. The first function is to be performed when we are accessing the files is to open a file. Opening a file establishes a link between the program and the operating system about which file we want to access for what purpose. We provide the operating system to which file we want to access and for what purpose. For accessing a file we just have to name the file and plan whether we want o read data from the file or write data onto the file. The syntax for opening is:
FILE *fp;
inbuilt structure
fp= fopen( “file name”, “mode”);
Union in C-language
Union is that data structure which is also user defined data type but to define a union keyword union is used instead of struct.
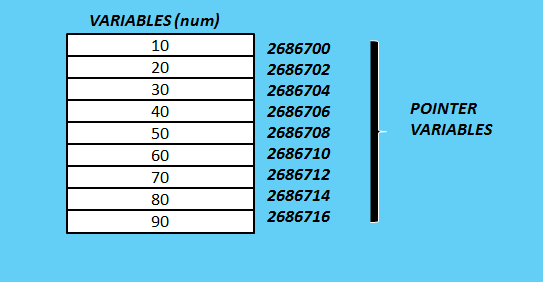
Pointers in C-language
Pointer is that variable which stores the memory address of another variable. It means pointer is itself a variable which stores hex-decimal address of the location.
January 22, 2013
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)