A File is a bunch of bytes stored on some storage device like magnetic disk or tape etc. Most of the application programs process large volume of data which is permanently stored in files. We can write programs that can read data from file(s) and write data to file(s).
Pages
▼
January 31, 2013
I/O File Handling in C++ (OOPs)
A File is a bunch of bytes stored on some storage device like magnetic disk or tape etc. Most of the application programs process large volume of data which is permanently stored in files. We can write programs that can read data from file(s) and write data to file(s).
Polymorphism in C++ (OOPs)
Polymorphism is made from two words POLY+MORPHISM which means more the one form. In C++ polymorphism is implemented by overloading a function or an operator. In Function Overloading a single function name is used to perform different tasks.
January 30, 2013
Constructors & Destructors in C++ (OOPs)
In C++, a class only creates a data type and the objects of a class are created and initialized as separate. A constructor (having the same name as that of a CLASS) is a member function which is automatically used to initialize the objects of the CLASS type with legal initial values.
Friend Function in C++ (OOPs)
A Friend Function is a non-member function that can access private data’s. A friend CLASS is a class whose member functions can access another class i.e. private and protected classes.
Classes & Objects in C++ (OOPs)
“C with classes” was the original name given by the originator Stroustrup initially, which now days is popular known form as C++ or OOPs (Object Oriented Programming). Classes and objects are the most important feature of C++. The Class implements OOPs features and ties then together. We have already seen that a structure groups different types of elements and a function organizes the program actions to perform the desired task.
Manipulators in C++ (OOPs)
Some standard manipulators are used in C++ (OOPs) which are stored under header file iomanip.h. Under this it has capabilities to show inter-conversions like binary, decimal, hex-decimal, set the precision for more accurate answer and various other functions like you can see in the programs.
Structures in C++ (OOPs)
Structure is the user defined data type which can store heterogeneous data i.e. data of different types. It means in structure member with all possible data type can be used and there is no restriction that elements of the structure are stored at adjacent memory locations. Structure is declared with key word struct followed by its name and then by block.
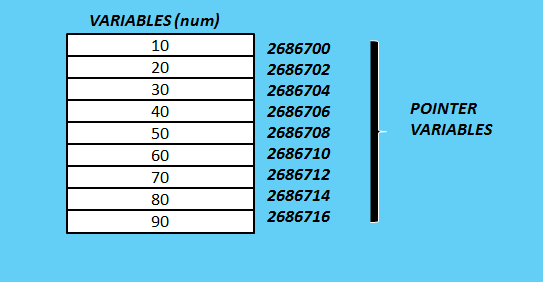
Pointers in C++ (OOPs)
Pointer is that variable which stores the memory address of another variable. It means pointer is itself a variable which stores hex-decimal address of the location.
January 29, 2013
Arrays in C++ (OOPs)
Array is an arrangement of same type of data at adjacent memory locations. Array is useful whenever large volume of data is to be processed and stored in the memory.
Suppose an average marks are to be calculated from all the students in the school. This is difficult to find the sum of marks of all students. In this situation an array is the best alternative. Its divided in two categories:
1. Single / 1-D Array
2. Multi-dimension Array
Loop Control- for loop in C++ (OOPs)
“for” loop is also structure control loop as program will run or execute if the initial condition is true otherwise it will terminate and program will run until some condition is fulfilled.
FORMAT:
for(expression1;expression2;expression3)
{
Statement1;
Statement2;
}
Switch Statement in C++ (OOPs)
This statement is also used for decision making. Here key word is switch followed by control variable and followed by it’s block.
In the block of switch statement multiple cases are used and each ends with break statement this is also called as early exit loop.
Out of all the cases only that case will run whose value matches with the control variable.
Loop Control- While & Do-while in C++ (OOPs)
These are used for repeating some portion of the program either by specified number of times or until a particular condition is true.
1. while statement
2. do while statement
3. for loop
Decision Making- If else statement in C++ (OOPs)
This statement is also a conditional statement. It starts with keyword ‘if’ followed by an expression followed by “ first statement” and “ second statement” is given after ‘else’ clause.
Format:
if(expression)
statement1;
else
statement2;
Simple C++ (OOPs) Programs
/* Program to enter two values and perform addition and multiplication operation*/
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
main()
{
int n1,n2,sum,mul;
cout<<"\n Enter any two numbers";
cin>>n1>>n2;
sum=n1+n2;
mul=n1*n2;
cout<<"\n Sum of two numbers is "<<sum;
cout<<"\n Multiplication of two numbers is "<<mul;
getch();
}
January 23, 2013
Files Input/Output in C-language
A file is a place on the disk where the group of related data are stored. The first function is to be performed when we are accessing the files is to open a file. Opening a file establishes a link between the program and the operating system about which file we want to access for what purpose. We provide the operating system to which file we want to access and for what purpose. For accessing a file we just have to name the file and plan whether we want o read data from the file or write data onto the file. The syntax for opening is:
FILE *fp;
inbuilt structure
fp= fopen( “file name”, “mode”);
Union in C-language
Union is that data structure which is also user defined data type but to define a union keyword union is used instead of struct.
Structure in C-language
Structure is the user defined data type which can store heterogeneous data i.e. data of different types. It means in structure member with all possible data type can be used and there is no restriction that elements of the structure are stored at adjacent memory locations. Structure is declared with key word struct followed by its name and then by block.
Pointers in C-language
Pointer is that variable which stores the memory address of another variable. It means pointer is itself a variable which stores hex-decimal address of the location.
January 22, 2013
Prototype Function
When a function is defined after the main function it needs to be declared in the declaration section of the program. This declaration section statement is known as function prototype.
This tells the calling function the type of value that will be returned with the name of the function and list of argument data types.
Syntax:
return type function name(Argument list);
int fun (f1,f2);
Function with parameter with return
This function can also return a value from the called function to the calling function i.e. the output which is printed in the main function whenever the value will be returned to the main function it can be printed thereafter. Now the function type should not be void because function will return a value. Therefore, it’s overall type is decided by the type of value it returned (int, float etc.).
Function with parameters with no return
Function can also use parameters and these parameters should be specified as a list along with function name with specific data types and each argument should be separated by ‘,’.
In function with parameter or arguments two types of arguments are used ACTUAL PARAMETERS and FORMAL OR DUMMY PARAMETERS.
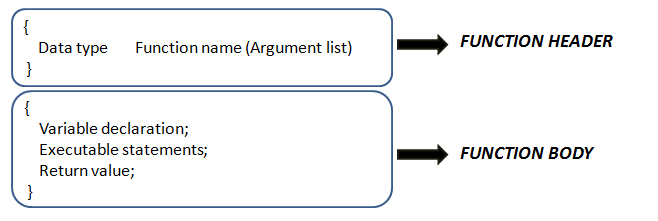
Function in C-language
A function is block of codes that performs a particular task, this block is given a name and whenever we want to execute this block we simply write the name of the function. Function is a small sub-program which is a self contained block of statements and the function which is defined by the user is User Defined Functions.
Arrays in C-language
Array is an arrangement of same type of data at adjacent memory locations. Array is useful whenever large volume of data is to be processed and stored in the memory.
Suppose an average marks are to be calculated from all the students in the school. This is difficult to find the sum of marks of all students. In this situation an array is the best alternative. Its divided in two categories:
1. Single / 1-D Array
2. Multi-dimension Array
January 21, 2013
Switch Statement
This statement is also used for decision making. Here key word is switch followed by control variable and followed by it’s block.
In the block of switch statement multiple cases are used and each ends with break statement this is also called as early exit loop.
Out of all the cases only that case will run whose value matches with the control variable.
Loop Control- for loop
“for” loop is also structure control loop as program will run or execute if the initial condition is true otherwise it will terminate and program will run until some condition is fulfilled.
FORMAT:
for(expression1;expression2;expression3)
{
Statement1;
Statement2;
}
Loop Control- While & Do while loop
These are used for repeating some portion of the program either by specified number of times or until a particular condition is true.
1. while statement
2. do while statement
3. for loop
Decision making- Nested If else
This statement can be used to select any one statement or a block which contains a set of instructions. Only that statement will execute which is true according to the data entered and rest other conditions will not executed.
FORMAT:
if(expression1)
Statement1;
else if(expression2)
statement2;
else if(expression3)
statement3;
Decision making- If else statement
This statement is also a conditional statement. It starts with keyword ‘if’ followed by an expression followed by “ first statement” and “ second statement” is given after ‘else’ clause.
Format:
if(expression)
statement1;
else
statement2;
January 20, 2013
Simple C-programs
/*Program to enter two numbers by user and perform addition and multiplication operations*/
#include<stdio.h>#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int n1,n2,sum=0,mul=0 ;
printf("\n enter any two numbers");
scanf("%d%d",&n1,&n2);
sum=n1+n2;
mul=n1*n2;
printf("\n sum of two numbers is %d",sum);
printf("\n multiplication of two numbers is %d",mul);
getch();
}















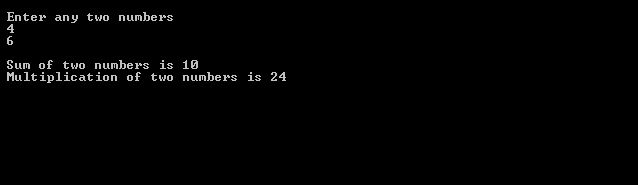















+codes.PNG)




